Angioedema is a medical condition that causes swelling deep within the skin’s layers. It can be extremely uncomfortable and sometimes even life-threatening. To effectively manage and treat angioedema, it’s crucial to have a deep understanding of its causes and triggers. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the underlying factors that contribute to angioedema and explore the various triggers that can set off this condition. If you start searching the options below, you can find the best deals for you.
Decoding Angioedema: Causes and Triggers
When it comes to allergic angioedema, the immune system plays a pivotal role. The body’s immune response is triggered by certain allergens, such as insect bites, medications, or certain foods. The immune system recognizes these substances as harmful and releases histamine, a chemical that causes blood vessels to leak fluid into the surrounding tissues. This leads to the characteristic swelling and itching experienced by individuals with allergic angioedema.
Non-allergic angioedema, on the other hand, takes a different path. Unlike its allergic counterpart, it does not involve an immune response. Instead, this type of angioedema can have various underlying causes. It may be triggered by certain medications, infections, autoimmune disorders, or even genetic factors. For example, some individuals may experience angioedema as a side effect of certain blood pressure medications, while others may have a genetic predisposition to the condition. Identifying these triggers is crucial to avoid future episodes of angioedema and effectively manage the condition.
Uncovering the Hidden Triggers of Angioedema
While allergic angioedema is commonly triggered by an immune response to certain allergens, such as insect bites, medications, or certain foods, non-allergic angioedema can have various underlying causes. These can include certain medications, infections, autoimmune disorders, and genetic factors. Identifying these triggers is crucial to avoid future episodes of angioedema.
Allergic vs. Non-Allergic Angioedema: What’s the Difference?
Allergic angioedema occurs when the immune system initiates an inflammatory response to an allergen. This triggers the release of histamine, leading to the characteristic swelling and itching. Non-allergic angioedema, on the other hand, does not involve an immune response; instead, it may be caused by factors such as a deficiency in certain enzymes or imbalances in specific hormones.
Identifying the Telltale Signs of Angioedema
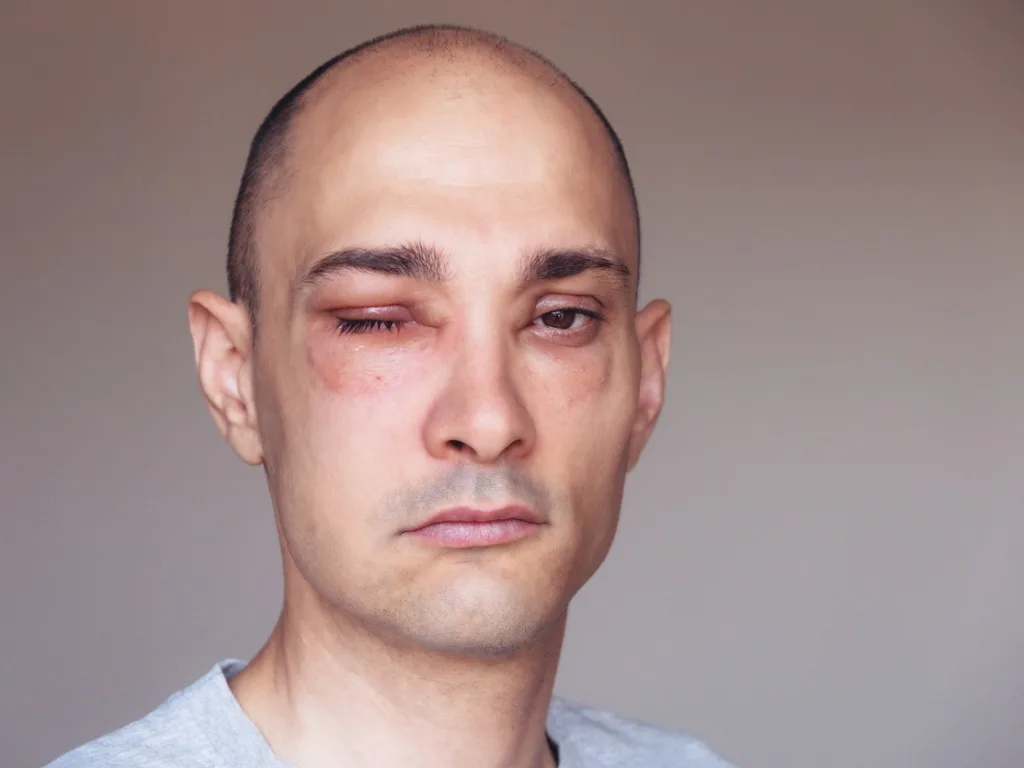
Recognizing the symptoms of angioedema is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Although the condition primarily affects the skin’s deeper layers, it can also involve the lips, tongue, throat, and even the internal organs in severe cases.
Understanding the Physical Symptoms of Angioedema
The most noticeable symptom of angioedema is localized swelling, which can be accompanied by redness and itchiness. In some cases, the swelling may occur on the face, hands, feet, or even the genital area. It is important to note that angioedema is not typically associated with hives, which are raised, itchy bumps on the skin.
The Importance of Diagnosis in Managing Angioedema
An accurate diagnosis is essential for the effective management of angioedema. A medical professional will evaluate the symptoms and medical history to identify the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnostic Tests for Angioedema: What to Expect
During the diagnostic process, various tests may be conducted to determine the cause of angioedema. These tests can include blood tests to check for allergic reactions or autoimmune disorders, skin tests to identify potential allergens, and imaging tests to evaluate the internal organs.
Medications and Therapies for Angioedema Relief
In many cases, antihistamines can effectively reduce swelling and relieve symptoms. In more severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to control inflammation. Additionally, other therapeutic measures, such as immune-modulating drugs or plasma-derived products, may be considered based on the individual’s condition.
Natural Remedies for Managing Angioedema Symptoms
While medical treatments are the primary approach to managing angioedema, some natural remedies can complement conventional therapies. These may include applying cold compresses to reduce swelling, avoiding triggers, and practicing stress-reduction techniques.
Medications That Can Help with Angioedema
In addition to the medications mentioned earlier, several other drugs can be used to manage angioedema more effectively. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable medication based on the specific type and cause of angioedema.
Understanding the Role of Antihistamines in Angioedema Treatment
Antihistamines are commonly used to manage allergic angioedema by blocking the effects of histamine, thereby reducing swelling and itchiness. These medications can be taken orally or applied topically, depending on the severity and location of the swelling.
Corticosteroids: A Powerful Tool Against Angioedema
Corticosteroids work by suppressing the immune response and reducing inflammation. They can be highly effective in managing severe cases of angioedema, but their long-term use should be carefully monitored due to potential side effects.
Lifestyle Changes to Alleviate Angioedema Symptoms
While medication and therapies play a crucial role in managing angioedema, making certain lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the likelihood of triggering an episode.
Dietary Modifications for Angioedema Management
In some cases, certain foods can trigger angioedema. It is important to identify and avoid these trigger foods to prevent episodes. Keeping a food diary and working with a healthcare professional or nutritionist can be helpful in determining any dietary triggers.
Stress has been identified as a potential trigger for angioedema. Engaging in stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling can help manage stress levels and reduce the frequency of episodes.