Oxygen therapy is a critical treatment for individuals with chronic respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and cystic fibrosis. The two primary sources of oxygen for home use are oxygen concentrators and oxygen tanks. This comprehensive guide will delve into the pros and cons of each, helping you make an informed decision. If you start searching the options below, you can find the best deals for you.
Oxygen Concentrators: An Overview
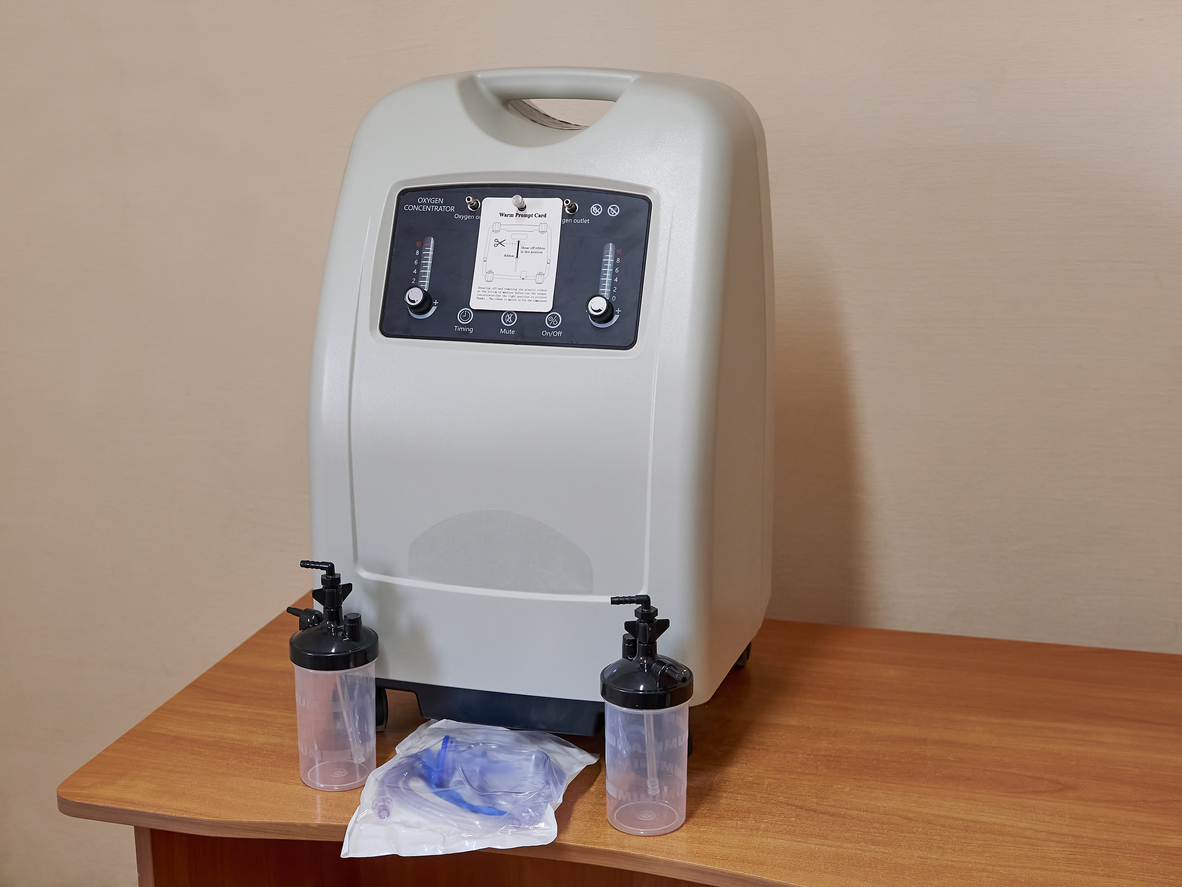
Oxygen concentrators are medical devices that take in air from the environment, remove gases that are not oxygen, and deliver purified oxygen to the user. They are powered by electricity and can be used continuously, making them a popular choice for home use.
There are two types of oxygen concentrators: stationary and portable. Stationary concentrators are larger and designed for home use, while portable concentrators are smaller, lighter, and designed for use while traveling.
Pros of Oxygen Concentrators
Oxygen concentrators offer several advantages. First, they provide a continuous supply of oxygen, as long as there is a power source. This makes them ideal for individuals who require oxygen therapy 24/7. They also eliminate the need for oxygen deliveries, as they generate oxygen from the surrounding air.
Second, oxygen concentrators are safer than oxygen tanks. They don’t store oxygen under pressure, reducing the risk of an oxygen-related fire. Additionally, they are quiet and easy to use, making them less disruptive in a home environment.
Cons of Oxygen Concentrators
Despite their advantages, oxygen concentrators also have some drawbacks. They require a reliable power source, which can be a challenge during power outages. While some models come with a backup battery, these typically only last for a few hours.
Furthermore, oxygen concentrators can be expensive. While insurance often covers part of the cost, individuals may still be responsible for a significant portion. Finally, while portable concentrators are available, they may not be as compact or lightweight as oxygen tanks, potentially limiting mobility.
Oxygen Tanks: An Overview
Oxygen tanks, or oxygen cylinders, store oxygen under pressure. They come in various sizes, from large, stationary tanks to small, portable ones. Oxygen tanks deliver oxygen through a regulator that controls the flow rate.
Like oxygen concentrators, there are two types of oxygen tanks: refillable and disposable. Refillable tanks can be used repeatedly, while disposable tanks are discarded after use.
Pros of Oxygen Tanks
Oxygen tanks also have several benefits. They do not require electricity, making them a reliable choice during power outages. Portable oxygen tanks are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for travel or short outings.
Furthermore, oxygen tanks can be less expensive upfront than oxygen concentrators. They can also deliver a high flow rate of oxygen, making them suitable for individuals with severe respiratory conditions.
Cons of Oxygen Tanks
However, oxygen tanks also have their disadvantages. They require regular refills or replacements, which can be inconvenient and costly over time. There is also a risk of running out of oxygen if a refill or replacement is not readily available.
In addition, oxygen tanks can pose a safety risk. Oxygen is a flammable gas, and when stored under pressure, there is a risk of an oxygen-related fire or explosion. Therefore, they must be stored and handled with care.
Choosing Between an Oxygen Concentrator and an Oxygen Tank
When choosing between an oxygen concentrator and an oxygen tank, several factors should be considered. These include the individual’s oxygen needs, lifestyle, budget, and personal preferences.
For individuals who require continuous oxygen therapy, an oxygen concentrator may be the best choice. However, for those who only need supplemental oxygen occasionally or during certain activities, an oxygen tank may be sufficient.
Ultimately, the decision should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider. They can provide guidance based on the individual’s specific condition and needs.
Both oxygen concentrators and oxygen tanks have their pros and cons. Understanding these can help individuals and their caregivers make an informed decision about the best oxygen therapy option for their needs. While the choice may seem daunting, remember that the goal is to improve quality of life and maintain independence while managing a chronic respiratory condition.