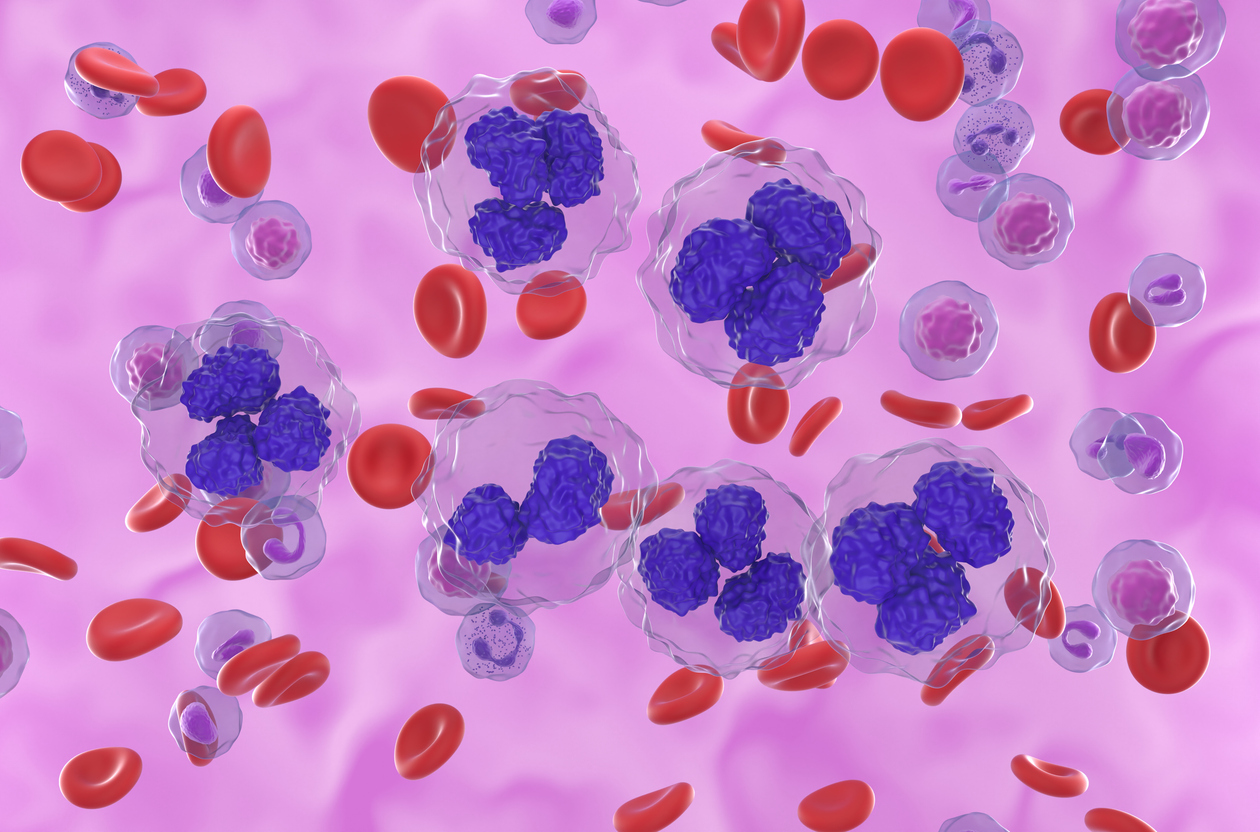
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, a vital component of the body’s immune system. This complex disease has many forms, each with its own characteristics and treatment options. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of lymphoma, its types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Lymphoma?
Lymphoma is a broad term for cancer that begins in cells of the lymph system. The lymph system is part of the body’s immune system and helps fight infections and diseases. There are two main types of lymphoma: Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL). Both types have different behaviours, treatment options, and prognoses.
While lymphoma can affect anyone, certain factors increase the risk. These include age, sex, and a weakened immune system. It’s important to note that having one or more risk factors does not necessarily mean you will develop lymphoma. Many people with risk factors never develop the disease, while others with no known risk factors do.
Types of Lymphoma
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Hodgkin’s lymphoma, also known as Hodgkin’s disease, is a less common type of lymphoma. It’s characterized by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells, a type of abnormal cell that distinguishes this disease from other types of lymphoma. Hodgkin’s lymphoma can occur at any age, but it is most common in early adulthood and late adulthood.
There are several subtypes of Hodgkin’s lymphoma, including classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Each subtype has unique features and may require different treatment approaches.
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is more common than Hodgkin’s lymphoma. It includes a wide range of lymphomas that do not have Reed-Sternberg cells. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma can start in different parts of the lymphatic system, such as the lymph nodes, spleen, or bone marrow.
There are many types of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, which can be divided into aggressive (fast-growing) and indolent (slow-growing) types. The most appropriate treatment depends on the type and stage of the lymphoma, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Symptoms of Lymphoma
Common symptoms of lymphoma include swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and night sweats. However, these symptoms can also be caused by other, less serious conditions. Therefore, it’s important to seek medical advice if you’re experiencing these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time.
Some people with lymphoma may experience additional symptoms, depending on where the lymphoma is in the body. For example, lymphoma in the abdomen may cause pain or swelling, while lymphoma in the brain can cause headaches, seizures, or changes in personality.
Diagnosis of Lymphoma
Diagnosing lymphoma involves a series of tests and procedures. The first step is usually a physical examination, during which your doctor will check for swollen lymph nodes and other signs of lymphoma. If lymphoma is suspected, further tests will be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
These tests may include blood tests, imaging tests, and a biopsy, where a small sample of tissue is removed for laboratory testing. The biopsy can determine whether you have lymphoma, the type of lymphoma, and the stage of the disease. This information is crucial in planning the most effective treatment.
Treatment of Lymphoma
Treatment for lymphoma depends on the type and stage of the disease, as well as the patient’s overall health. The main treatment options for lymphoma are chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and stem cell transplant.
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing, while radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Immunotherapy helps your immune system fight cancer, and targeted therapy uses drugs that specifically attack cancer cells without harming normal cells. A stem cell transplant can replace diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow.
It’s important to discuss the benefits and risks of each treatment option with your healthcare team. This will help you make an informed decision about your treatment plan.
Living with Lymphoma
Living with lymphoma can be challenging, but many resources are available to help you cope. Support groups, counseling, and educational materials can provide emotional support and help you understand your disease and treatment options.
Regular follow-up care is crucial for people with lymphoma. This includes regular check-ups with your healthcare team, as well as tests to monitor your health and the effects of treatment. With the right care and support, many people with lymphoma can lead full and productive lives.
Remember, every person’s experience with lymphoma is unique. It’s important to stay informed, ask questions, and seek support when needed. With the right information and resources, you can navigate your lymphoma journey with confidence.